<script type="text/javascript"> _linkedin_partner_id = "6415570"; window._linkedin_data_partner_ids = window._linkedin_data_partner_ids || []; window._linkedin_data_partner_ids.push(_linkedin_partner_id); </script><script type="text/javascript"> (function(l) { if (!l){window.lintrk = function(a,b){window.lintrk.q.push([a,b])}; window.lintrk.q=[]} var s = document.getElementsByTagName("script")[0]; var b = document.createElement("script"); b.type = "text/javascript";b.async = true; b.src = "https://snap.licdn.com/li.lms-analytics/insight.min.js"; s.parentNode.insertBefore(b, s);})(window.lintrk); </script> <noscript> <img height="1" width="1" style="display:none;" alt="" src="
×
IN2 utilise a combination of Dynamic Simulation Modelling (DSM) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) in order to undertake detailed comfort analysis throughout the design process, predicting in particular temperatures, radiation and air quality to ensure optimum comfort and wellbeing for the built environment.
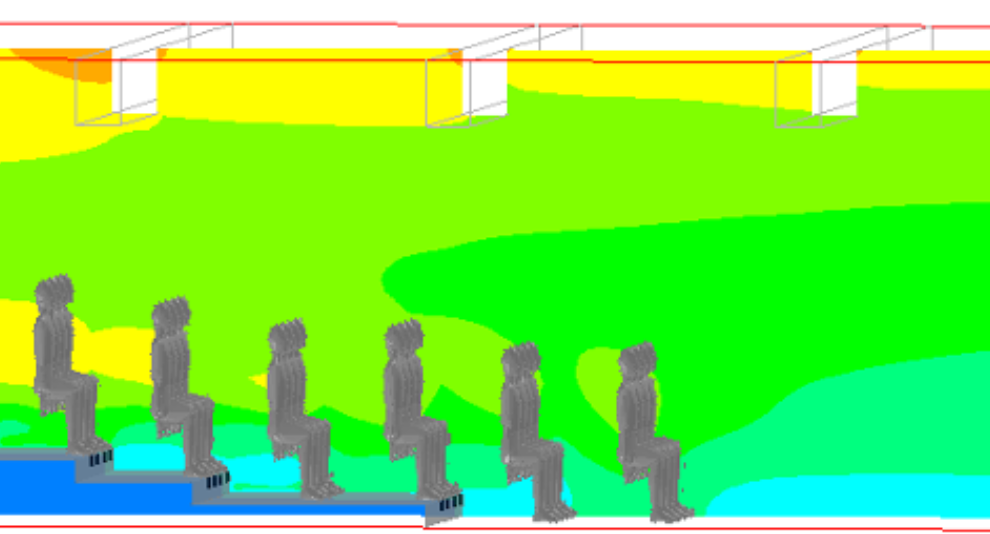
Where particular spaces within buildings benefit from more detailed thermal analysis, CFD techniques are utilised to predict temperatures, velocities and associated comfort parameters at a high degree of resolution, ensuring localised discomfort effects are mitigiated against. CFD also enables clear visual representation of often complex internal environmental conditions, utilising contours, vectors and streamlines.
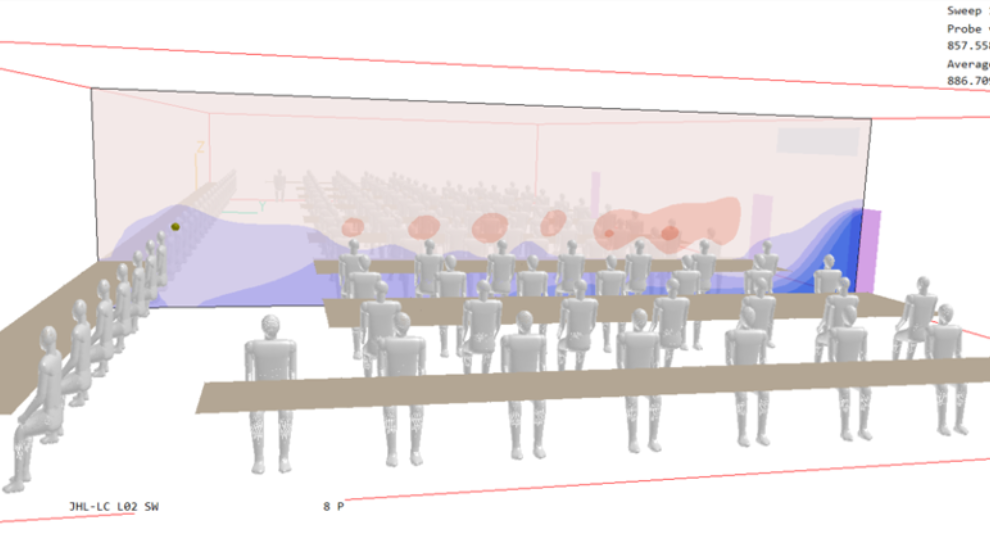
In addition to enabling detailed analysis of thermal comfort conditions, IN2 utilise CFD techniques to ensure wellbeing in buildings, by assessing ventilation and particle concentration, both in terms of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) and contaminant risk for internal and external environments.
IN2’s experience and expertise in utilising CFD techniques in the Built Environment, enable us to assess ventilation solutions for airborne viral transmission risk, as has been identified for Covid-19 and its variants. This detailed analysis ensures that ventilation design can be developed to minimise airborne transmission risk and thus increase wellbeing for the internal environment.
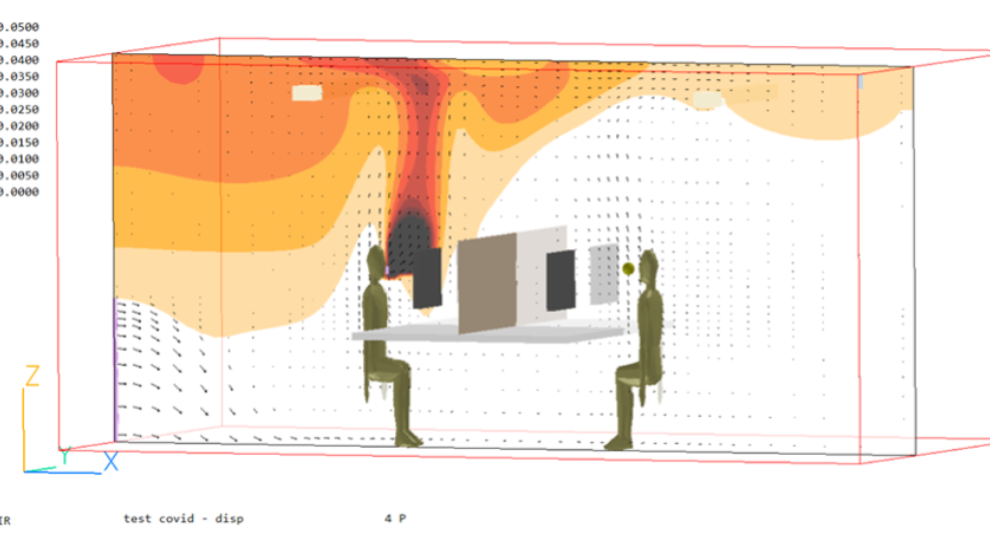
When planning and designing Comfort & Wellbeing solutions, we recognise the importance of ensuring that these services put people first while integrating with the design and objectives of the building project.
When planning and designing Comfort & Wellbeing solutions, we recognise the importance of ensuring that these services put people first while integrating with the design and objectives of the building project.